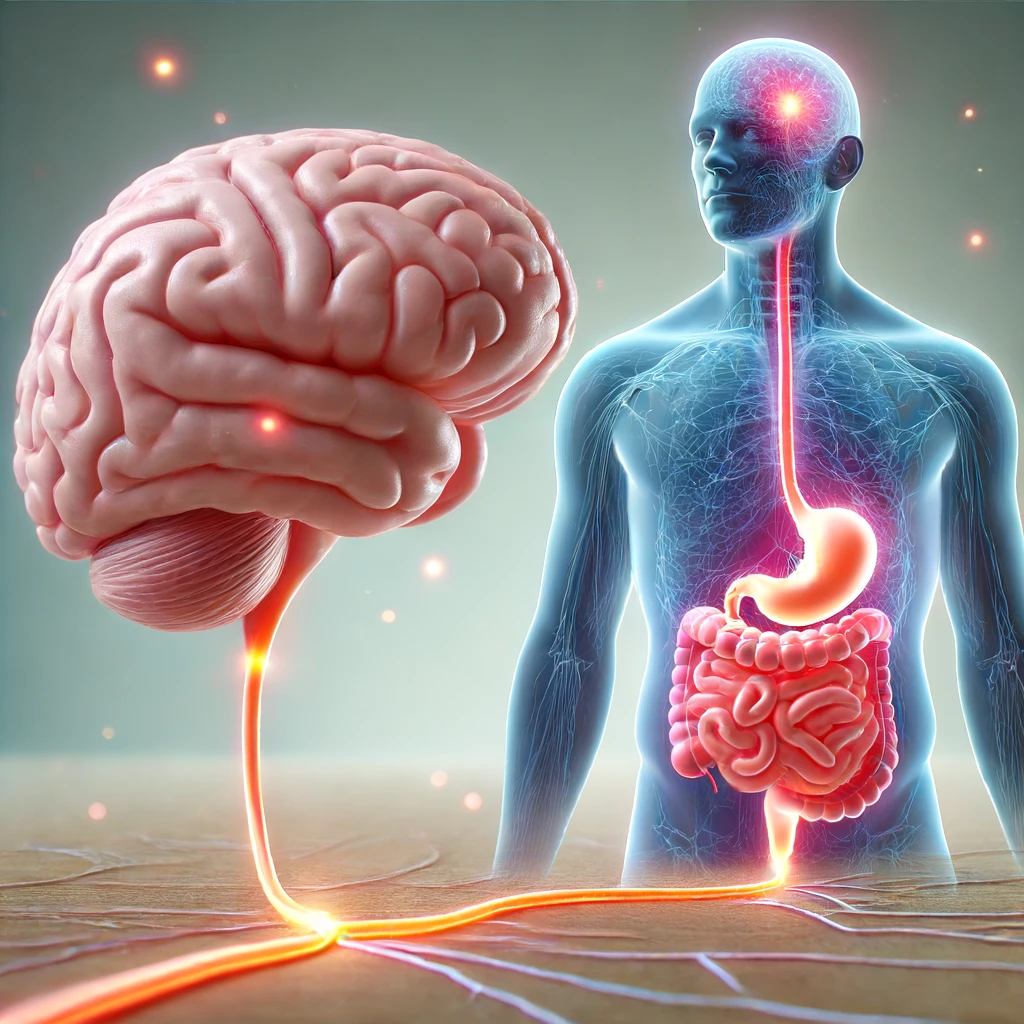
How Your Brain Affects Your Gut Health
You’ve heard the phrase “gut feeling,” but did you know that your brain and gut are actually connected? This connection is more than just a figure of speech.
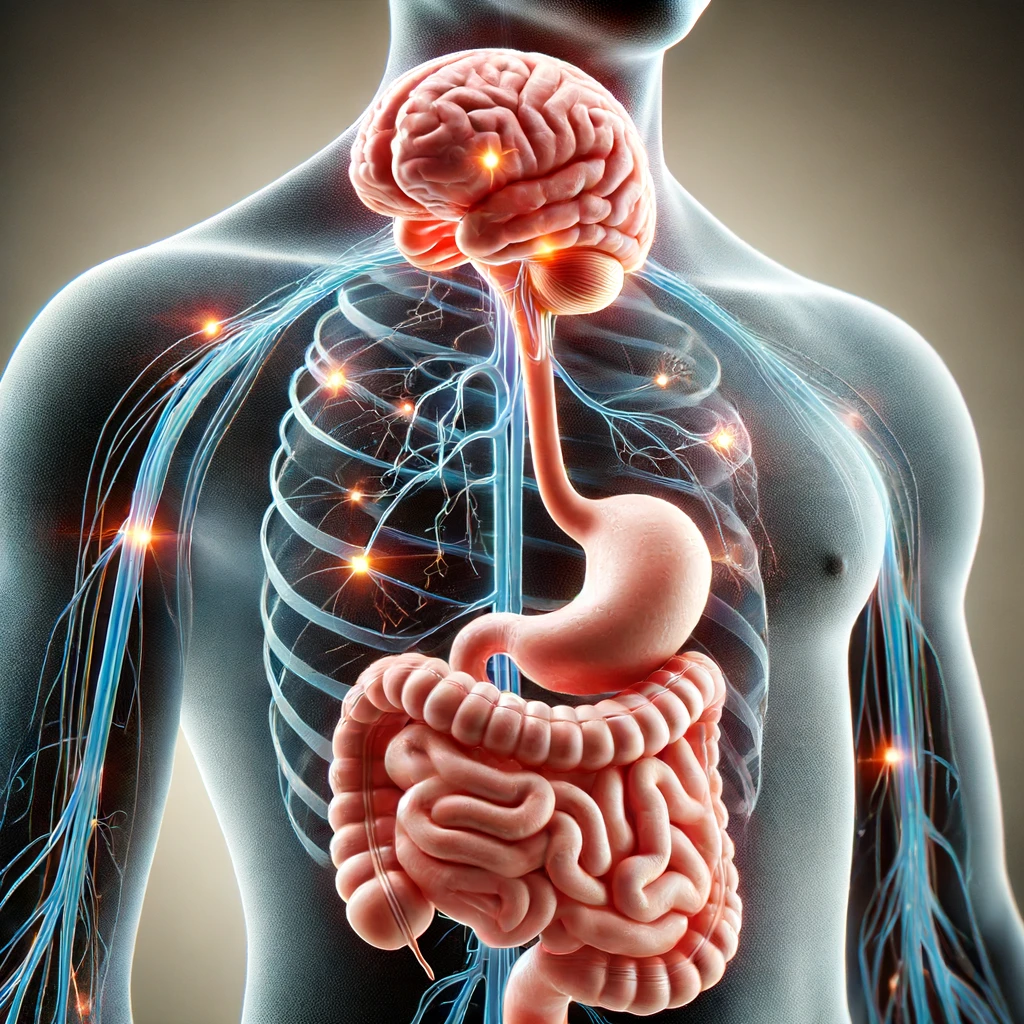
It’s a real, physical link between your brain and digestive system. Understanding this link can help you manage your gut health better and improve your overall well-being. Let’s dive into how your brain affects your gut health.
The Brain-Gut Connection
Your brain and gut are connected through a network of nerves, chemicals, and hormones. This is called the gut-brain axis.
The main highway of communication between your brain and gut is the vagus nerve. This nerve runs from your brainstem to your abdomen and sends signals in both directions. It’s like a superhighway of information that helps keep your brain and gut in sync.
Stress and Your Gut
Stress is one of the biggest factors that can affect your gut health. When you’re stressed, your brain sends signals to your gut that can disrupt its normal function. This can lead to issues like stomach pain, diarrhea, and constipation.
Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that prepares your body for a “fight or flight” response. While this response is useful in dangerous situations, it can cause problems when it’s triggered too often. Cortisol can slow down your digestion, leading to discomfort and other gut issues.
Emotions and Digestion
Your emotions can also impact your gut.
Have you ever felt “butterflies” in your stomach when you’re nervous? That’s your gut responding to your emotional state. Anxiety, sadness, and excitement can all cause changes in your digestive system.
For example, anxiety can speed up your digestion, leading to diarrhea. On the other hand, sadness can slow down your digestion, causing constipation. By understanding how your emotions affect your gut, you can take steps to manage your emotional health and, in turn, improve your gut health.
Gut Microbiota
Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria, known as gut microbiota. These bacteria play a crucial role in your digestion and overall health. They help break down food, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful bacteria.
Your brain can influence the composition of your gut microbiota. Stress and other emotional states can change the balance of bacteria in your gut. This can lead to problems like inflammation and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
The Role of Diet
What you eat can also affect the brain-gut connection. Certain foods can help keep your gut and brain healthy. For example, fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote the growth of good bacteria in your gut. These bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids that help reduce inflammation and support brain health.
Probiotics, found in yogurt and fermented foods, can also benefit your gut and brain. They add beneficial bacteria to your gut and can help improve your mood and reduce anxiety.
Exercise and Gut Health
Regular exercise is another way to support the brain-gut connection. Exercise helps reduce stress and promotes a healthy balance of gut bacteria. It also stimulates the release of endorphins, which are chemicals that improve your mood and reduce pain.
Even moderate exercise, like walking or yoga, can have a positive impact on your gut health. By staying active, you can keep both your brain and gut in good shape.
Sleep and Your Gut
Getting enough sleep is essential for both brain and gut health. Sleep helps regulate the hormones that control your appetite and digestion. When you don’t get enough sleep, these hormones can get out of balance, leading to issues like weight gain and digestive problems.
Poor sleep can also increase stress levels, which can further impact your gut health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to keep your brain and gut functioning properly.
Practical Tips for a Healthy Brain-Gut Connection
Now that you know how your brain affects your gut health, here are some practical tips to keep both in good shape:
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or spending time in nature. These can help keep your stress levels in check and support your gut health.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include plenty of fiber-rich foods, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet. Add probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and fermented foods to support your gut microbiota.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, cycling, or yoga can help reduce stress and promote a healthy gut.
- Get Enough Sleep: Prioritize getting 7-9 hours of sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve your sleep quality.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support digestion and overall health.
- Pay Attention to Your Emotions: Recognize how your emotions impact your gut and take steps to manage your emotional health. Talking to a therapist or practicing mindfulness can help you cope with negative emotions.
The Importance of Mindfulness
Mindfulness is a powerful tool for managing the brain-gut connection. By practicing mindfulness, you can become more aware of how your thoughts and emotions affect your body. This awareness can help you make healthier choices and reduce stress.
Mindfulness techniques like meditation and deep breathing can help calm your mind and reduce the impact of stress on your gut. By incorporating mindfulness into your daily routine, you can improve both your mental and physical health.
The Science Behind the Brain-Gut Connection
Researchers are still learning about the complex relationship between the brain and gut. Studies have shown that the gut can send signals to the brain and vice versa. This communication is crucial for maintaining overall health.
For example, the gut produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, which is often called the “happy hormone.” Serotonin helps regulate mood, and a large portion of it is produced in the gut. This means that a healthy gut can contribute to a healthy mind.
Research has also shown that people with digestive disorders like IBS often have higher levels of anxiety and depression. This highlights the importance of a healthy brain-gut connection in managing both mental and physical health.
The Future of Brain-Gut Research
As researchers continue to study the brain-gut connection, we can expect to learn more about how to optimize this relationship for better health. Future treatments for digestive disorders may include therapies that target both the brain and gut.
For now, understanding the basics of the brain-gut connection can help you take steps to improve your health. By managing stress, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep, you can support a healthy brain and gut.
Your brain and gut are more connected than you might think. The brain-gut connection plays a crucial role in your overall health, affecting everything from digestion to mood. By taking steps to support this connection, you can improve both your mental and physical well-being.
Remember to manage stress, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Pay attention to how your emotions impact your gut and practice mindfulness to keep your brain and gut in sync. With these simple strategies, you can enjoy better health and a happier life.